一、Vuex状态管理的思想
- 数据封装,集中式管理,可见的数据变更【单项数据流】
- 解决跨组件之间的数据共享
- 同步数据和异步数据更新试图
还不会使用的同学可以看相关文档
- vuex官方文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/
- vuex源码地址:https://github.com/vuejs/vuex 【可以看src文件下内容/也可以看dist打包后的js文件】
- 个人使用文档:http://gongpengji.com/index.php/archives/22/
1.1)什么时候使用vuex
借用redux作者的话:(你品这句话)
Flux 架构就像眼镜:您自会知道什么时候需要它。
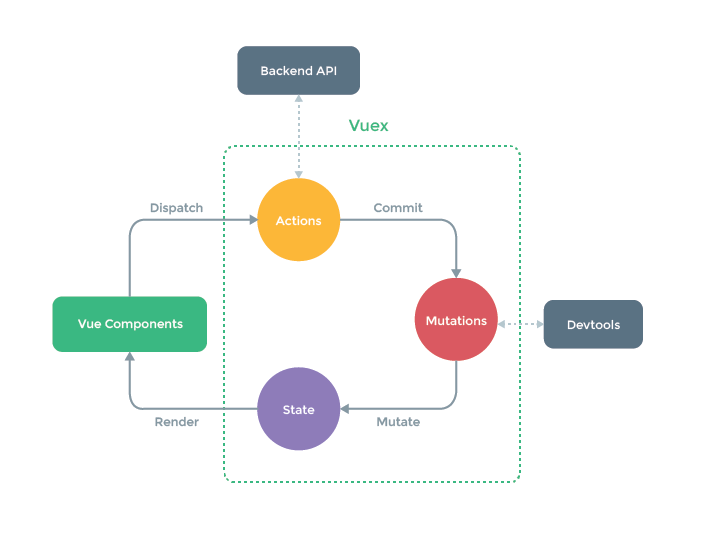
1.2)流程大体分为三步
- actions派发任务
- mutations执行任务
- state维护的数据状态
1.3) 实现一个vuex插件需要拆解几部分
二、实现自己的vuex并能支撑基本功能
前三步都是使用,和原来的使用方式是一样的,主要看最后一个文件那就是一个小型的vuex
2-1)main.js中使用
import store from './juziStore'
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')2-2)App.vue中调用
<div @click="$store.commit('add')">mutations-count:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div @click="$store.dispatch('add')">actions-count:{{ $store.state.count }}</div>
<div>getters-count:{{ $store.getters.dobolde }}</div>2-3)创建juziStore文件夹里面 - index.js
- 细心的朋友发现我这里有一行注释了的代码,其实这个注释的代码以前是这样的【import Store from 'vuex'】,这样store就是从我们下载的npm包中引用store类
- 但是我这里是vuex.common.js,其实这就是vuex的源码,我会直接引用,并断点。学习源码使用的
- 推荐代码地址:【里面有vuex.js/vuex.common.js等等,我们都可以直接拿来学习断点,不断查看运行步骤】https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/9039c2169634925682ffcb21c57f5df355e16ad1/dist
import Vue from 'vue'
// import MyStore from './vuex.common'
import MyStore from './myStore'
Vue.use(MyStore)
export default new MyStore.Store({
state: {
count: 0
},
mutations: {
add (state) {
state.count++
}
},
actions: {
add ({ commit }) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('add')
}, 222);
}
},
getters: {
dobolde: (state) => {
return state.count * 2
}
},
modules: {
}
})
2-4)创建juziStore文件夹里面 - myStore.js
- 注意看注解
// 1、实现状态管理仓库 store
// 2、实现install插件
// 3、实现响应式state
// 4、实现commit方法
// 5、实现dispath方法
// 6、实现getter方法
// 7、暴露store模块
// 喜闻乐见的Vue借用又来了
let Vue;
class Store {
constructor(options) {
// 保存配置
this.$options = options
// 指定上下文执行环境
this.commit = this.commit.bind(this)
this.dispatch = this.dispatch.bind(this)
// 保存this
this.getters = {}
// 拿到参数中的getters对象
this._wrappendGetters = options.getters
let computed = {};
const store = this
// 遍历对象
Object.keys(this._wrappendGetters).forEach(key => {
// 当前的getters中的函数
let fn = store._wrappendGetters[key]
// 借用computed计算属性,并返回携带当前state的函数,记得在下方new vue的时候加上computed
computed[key] = function() {
return fn(store.state)
};
// 对这个getter对象监听
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
// 响应式state
this._vm = new Vue({
data: {
// 利用vue的机制,加上$$ state就不会被代理,这样用户就不能通过_vm直接访问到state
$$state: options.state
},
computed
})
}
// 有访问state到时候,返回内部的$$state
// 存取器
get state () {
// 使用vue实例下面的观察属性_data,这是一个响应式对象
return this._vm._data.$$state
}
set state (v) {
console.error('不能直接修改state')
}
commit (type, payload) {
// 我们去那options里面的mutations
const _fn = this.$options.mutations[type]
if (!_fn) {
console.error(type + '的mutations不存在')
return
}
_fn(this.state, payload)
}
dispatch (type, payload) {
// 我们去那options里面的actions
const _fn = this.$options.actions[type]
if (!_fn) {
console.error(type + '的actions不存在')
return
}
_fn(this, payload)
}
}
function install (_Vue) {
// 看过我之前写的my-vue-router,就知道这里,在外部use这个插件的时候,我们就能拿到Vue实例
Vue = _Vue
// 这里在讲一下吧
// 因为在执行use的时候,我们是拿不到new vue时候里面的参数的,vue对象还没执行。
// 借用混入,等待生命周期创建的时候,在挂载到Vue实例中
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate () {
if (this.$options.store) {
Vue.prototype.$store = this.$options.store
}
}
})
}
export default { Store, install }最后,手写的vuex,就完成基本功能啦,还不快去玩耍玩耍
三、手撕vuex源码
- 想看全部代码,在一个js中的可以看
推荐代码地址:【里面有vuex.js/vuex.common.js等等,我们都可以直接拿来学习断点,不断查看运行步骤】https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/9039c2169634925682ffcb21c57f5df355e16ad1/dist
- 想看作者如何设计编写整个vuex的过程的,通用方法和功能分离就看https://github.com/vuejs/vuex/tree/dev/src
- 我们今天就主要看三个文件 - 有兴趣的可以查看其他文件和功能
3-1)源码:utils.js
- 里面大部分都是对对象处理的方法,有个印象就可以了,当读到人家实现store类的时候,知道这里有它直接调用的方法, 对对象进行封装
/**
* Get the first item that pass the test
* by second argument function
*
* @param {Array} list
* @param {Function} f
* @return {*}
*/
export function find (list, f) {
return list.filter(f)[0]
}
/**
* Deep copy the given object considering circular structure.
* This function caches all nested objects and its copies.
* If it detects circular structure, use cached copy to avoid infinite loop.
*
* @param {*} obj
* @param {Array<Object>} cache
* @return {*}
*/
export function deepCopy (obj, cache = []) {
// just return if obj is immutable value
if (obj === null || typeof obj !== 'object') {
return obj
}
// if obj is hit, it is in circular structure
const hit = find(cache, c => c.original === obj)
if (hit) {
return hit.copy
}
const copy = Array.isArray(obj) ? [] : {}
// put the copy into cache at first
// because we want to refer it in recursive deepCopy
cache.push({
original: obj,
copy
})
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => {
copy[key] = deepCopy(obj[key], cache)
})
return copy
}
/**
* forEach for object
*/
export function forEachValue (obj, fn) {
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key => fn(obj[key], key))
}
export function isObject (obj) {
return obj !== null && typeof obj === 'object'
}
export function isPromise (val) {
return val && typeof val.then === 'function'
}
export function assert (condition, msg) {
if (!condition) throw new Error(`[vuex] ${msg}`)
}
export function partial (fn, arg) {
return function () {
return fn(arg)
}
}3-2)源码:mixin.js
- ˙这里面的代码也不多,主要干了两件事
- 对vue不同版本的兼容处理
- 在vue实例上挂载$store
export default function (Vue) {
const version = Number(Vue.version.split('.')[0])
if (version >= 2) {
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })
} else {
// override init and inject vuex init procedure
// for 1.x backwards compatibility.
const _init = Vue.prototype._init
Vue.prototype._init = function (options = {}) {
options.init = options.init
? [vuexInit].concat(options.init)
: vuexInit
_init.call(this, options)
}
}
/**
* Vuex init hook, injected into each instances init hooks list.
*/
function vuexInit () {
const options = this.$options
// store injection
if (options.store) {
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
this.$store = options.parent.$store
}
}
}3-3)最后重头戏:源码store.js 【部分注解】
我截取部分,4、5百行还是有点多的[主要思考上面我手写的,和人家源码实现的地方]
我会以我自己理解的方式来给源码注解,如有错误,请指正包涵
// 调用mixin方法,给vue挂载store的
import applyMixin from './mixin'
// 结合devtool,可以在mutations数据的时候,查看状态管理中的store仓库
import devtoolPlugin from './plugins/devtool'
import ModuleCollection from './module/module-collection'
// 解构出刚刚通用工具方法,大部分是处理obj
import { forEachValue, isObject, isPromise, assert, partial } from './util'
// 喜闻乐见,写vue插件都有的借用Vue
let Vue // bind on install
// 定义store类
export class Store {
constructor (options = {}) {
const {
plugins = [],
strict = false
} = options
// 给我们的store仓库初始化
this._committing = false
this._actions = Object.create(null)
this._actionSubscribers = []
this._mutations = Object.create(null)
this._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options)
this._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
this._subscribers = []
this._watcherVM = new Vue()
this._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)
// bind commit and dispatch to self
const store = this
const { dispatch, commit } = this
this.dispatch = function boundDispatch (type, payload) {
return dispatch.call(store, type, payload)
}
this.commit = function boundCommit (type, payload, options) {
return commit.call(store, type, payload, options)
}
// strict mode
this.strict = strict
const state = this._modules.root.state
// init root module.
// this also recursively registers all sub-modules
// and collects all module getters inside this._wrappedGetters
// 初始化所有模块信息
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root)
// initialize the store vm, which is responsible for the reactivity
// (also registers _wrappedGetters as computed properties)
// 执行store的数据变化
resetStoreVM(this, state)
}
// 寄存器
get state () {
return this._vm._data.$$state
}
set state (v) {
if (__DEV__) {
assert(false, `use store.replaceState() to explicit replace store state.`)
}
}
// 这就是commit方法,去执行mutations中的方法
commit (_type, _payload, _options) {
// check object-style commit
const {
type,
payload,
options
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
const mutation = { type, payload }
// 在这里拿到mutations里面的方法
const entry = this._mutations[type]
if (!entry) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown mutation type: ${type}`)
}
return
}
this._withCommit(() => {
// 可能有多个mutations方法,通过遍历并执行
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
}
// dispatch方法,执行actions中的方法,我们发现方法里面
// 是使用promise包裹的函数返回结果,这是一个异步方法
// 如何去那到actions中的方法,和上面mutataions一样
dispatch (_type, _payload) {
// check object-style dispatch
const {
type,
payload
} = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload)
const action = { type, payload }
const entry = this._actions[type]
if (!entry) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown action type: ${type}`)
}
return
}
const result = entry.length > 1
? Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
: entry[0](payload)
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
result.then(res => {
try {
this._actionSubscribers
.filter(sub => sub.after)
.forEach(sub => sub.after(action, this.state))
} catch (e) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.warn(`[vuex] error in after action subscribers: `)
console.error(e)
}
}
resolve(res)
}, error => {
try {
this._actionSubscribers
.filter(sub => sub.error)
.forEach(sub => sub.error(action, this.state, error))
} catch (e) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.warn(`[vuex] error in error action subscribers: `)
console.error(e)
}
}
reject(error)
})
})
}
watch (getter, cb, options) {
if (__DEV__) {
assert(typeof getter === 'function', `store.watch only accepts a function.`)
}
return this._watcherVM.$watch(() => getter(this.state, this.getters), cb, options)
}
replaceState (state) {
this._withCommit(() => {
this._vm._data.$$state = state
})
}
}
function resetStore (store, hot) {
store._actions = Object.create(null)
store._mutations = Object.create(null)
store._wrappedGetters = Object.create(null)
store._modulesNamespaceMap = Object.create(null)
const state = store.state
// init all modules
installModule(store, state, [], store._modules.root, true)
// reset vm
resetStoreVM(store, state, hot)
}
// 这个方法里面就包裹着getters的执行方法
// 我自己写的getter,就是抄源码的,遍历对象、借用computed,最后兼容并返回
function resetStoreVM (store, state, hot) {
const oldVm = store._vm
// bind store public getters
store.getters = {}
// reset local getters cache
store._makeLocalGettersCache = Object.create(null)
const wrappedGetters = store._wrappedGetters
const computed = {}
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
// direct inline function use will lead to closure preserving oldVm.
// using partial to return function with only arguments preserved in closure environment.
computed[key] = partial(fn, store)
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
// use a Vue instance to store the state tree
// suppress warnings just in case the user has added
// some funky global mixins
const silent = Vue.config.silent
Vue.config.silent = true
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
})
Vue.config.silent = silent
// enable strict mode for new vm
if (store.strict) {
enableStrictMode(store)
}
if (oldVm) {
if (hot) {
// dispatch changes in all subscribed watchers
// to force getter re-evaluation for hot reloading.
store._withCommit(() => {
oldVm._data.$$state = null
})
}
Vue.nextTick(() => oldVm.$destroy())
}
}
function installModule (store, rootState, path, module, hot) {
// 里面我删除了,想看的可以去github上看,把其他环境的状态方法全部拿到并遍历
}
/**
* make localized dispatch, commit, getters and state
* if there is no namespace, just use root ones
*/
function makeLocalContext (store, namespace, path) {
const noNamespace = namespace === ''
const local = {
dispatch: noNamespace ? store.dispatch : (_type, _payload, _options) => {
const args = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
const { payload, options } = args
let { type } = args
if (!options || !options.root) {
type = namespace + type
if (__DEV__ && !store._actions[type]) {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown local action type: ${args.type}, global type: ${type}`)
return
}
}
return store.dispatch(type, payload)
},
commit: noNamespace ? store.commit : (_type, _payload, _options) => {
const args = unifyObjectStyle(_type, _payload, _options)
const { payload, options } = args
let { type } = args
if (!options || !options.root) {
type = namespace + type
if (__DEV__ && !store._mutations[type]) {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown local mutation type: ${args.type}, global type: ${type}`)
return
}
}
store.commit(type, payload, options)
}
}
// getters and state object must be gotten lazily
// because they will be changed by vm update
Object.defineProperties(local, {
getters: {
get: noNamespace
? () => store.getters
: () => makeLocalGetters(store, namespace)
},
state: {
get: () => getNestedState(store.state, path)
}
})
return local
}
function makeLocalGetters (store, namespace) {
if (!store._makeLocalGettersCache[namespace]) {
const gettersProxy = {}
const splitPos = namespace.length
Object.keys(store.getters).forEach(type => {
// skip if the target getter is not match this namespace
if (type.slice(0, splitPos) !== namespace) return
// extract local getter type
const localType = type.slice(splitPos)
// Add a port to the getters proxy.
// Define as getter property because
// we do not want to evaluate the getters in this time.
Object.defineProperty(gettersProxy, localType, {
get: () => store.getters[type],
enumerable: true
})
})
store._makeLocalGettersCache[namespace] = gettersProxy
}
return store._makeLocalGettersCache[namespace]
}
function registerMutation (store, type, handler, local) {
const entry = store._mutations[type] || (store._mutations[type] = [])
entry.push(function wrappedMutationHandler (payload) {
handler.call(store, local.state, payload)
})
}
function registerGetter (store, type, rawGetter, local) {
if (store._wrappedGetters[type]) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(`[vuex] duplicate getter key: ${type}`)
}
return
}
store._wrappedGetters[type] = function wrappedGetter (store) {
return rawGetter(
local.state, // local state
local.getters, // local getters
store.state, // root state
store.getters // root getters
)
}
}
function unifyObjectStyle (type, payload, options) {
if (isObject(type) && type.type) {
options = payload
payload = type
type = type.type
}
if (__DEV__) {
assert(typeof type === 'string', `expects string as the type, but found ${typeof type}.`)
}
return { type, payload, options }
}
// 给vue写插件,还要写个install方法,接收Vue作为参数,在这里我们就能拿到vue了
export function install (_Vue) {
if (Vue && _Vue === Vue) {
if (__DEV__) {
console.error(
'[vuex] already installed. Vue.use(Vuex) should be called only once.'
)
}
return
}
Vue = _Vue
applyMixin(Vue)
}
?叙事类评语?
你的文章内容非常用心,让人感动。 http://www.55baobei.com/YeJWbox7a4.html
想想你的文章写的特别好https://www.ea55.com/